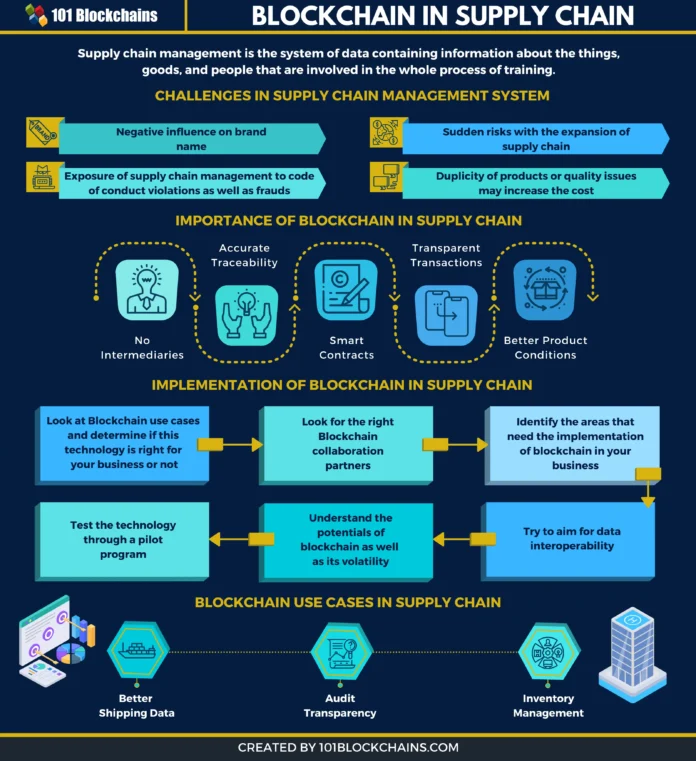
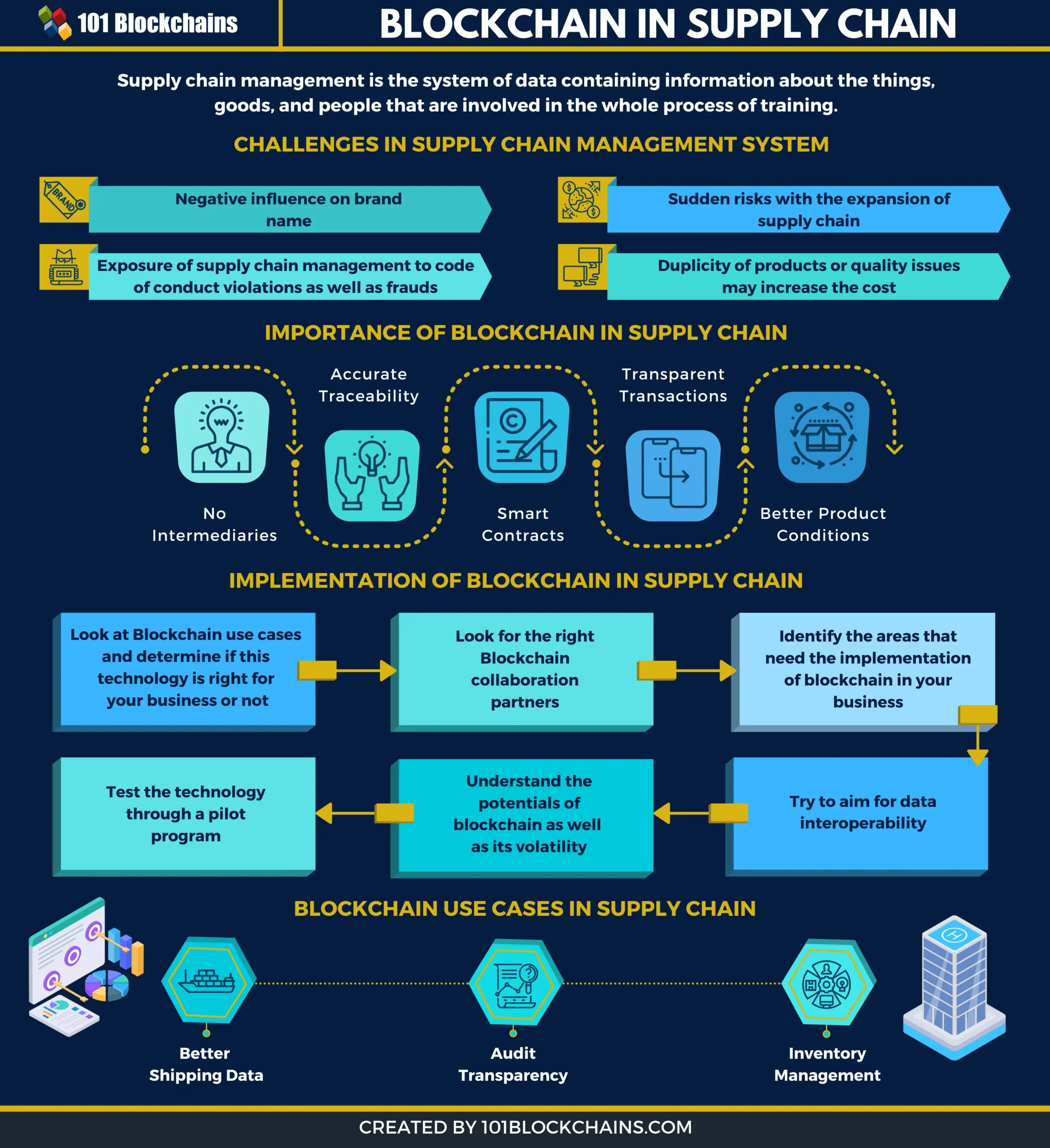
In 2024, blockchain technology continues to revolutionize various industries, with one of the most significant impacts being on supply chain transparency. This innovation addresses long-standing challenges related to tracking, verifying, and optimizing supply chains. As businesses strive for greater efficiency and consumers demand more transparency, blockchain emerges as a powerful tool to meet these needs.
Introduction to Blockchain and Supply Chain Management
Blockchain, a decentralized digital ledger, records transactions across multiple computers to ensure data integrity and security. In the context of supply chains, it offers a transparent and immutable record of every transaction, from raw material sourcing to final product delivery. This transparency is crucial for building trust among stakeholders, reducing fraud, and improving operational efficiency.
Enhancing Traceability and Accountability
One of the primary benefits of blockchain in supply chains is enhanced traceability. Each product can be assigned a unique identifier recorded on the blockchain, allowing stakeholders to trace its journey through the supply chain in real-time. This capability is particularly vital for industries like food and pharmaceuticals, where tracking the origin and handling of products is critical for safety and compliance.
For instance, in the food industry, blockchain can track a product from the farm to the table. If a contamination issue arises, the blockchain record can quickly pinpoint the source, facilitating swift and targeted recalls. This not only protects consumers but also minimizes financial losses and reputational damage for companies.
Reducing Fraud and Counterfeiting
Counterfeiting and fraud are significant issues in global supply chains, affecting everything from luxury goods to essential medicines. Blockchain’s immutability makes it nearly impossible for counterfeit products to enter the supply chain undetected. Each transaction is time-stamped and verified by multiple parties, creating a permanent record that is extremely difficult to alter.
For example, the pharmaceutical industry, which loses billions annually to counterfeit drugs, can greatly benefit from blockchain. By tracking every step of the manufacturing and distribution process, blockchain ensures that only genuine products reach consumers. This transparency not only protects public health but also upholds the integrity of pharmaceutical companies.
Improving Efficiency and Reducing Costs
Blockchain can streamline supply chain operations by automating and digitizing processes that traditionally involve extensive paperwork and manual verification. Smart contracts, which are self-executing contracts with the terms directly written into code, can automate various tasks, such as verifying delivery, releasing payments, and updating inventory records.
These efficiencies reduce the time and cost associated with traditional supply chain management. For instance, shipping documents can be digitized and shared instantly across the blockchain, eliminating the need for intermediaries and reducing the risk of human error. This leads to faster processing times, lower administrative costs, and more reliable supply chains.
Enhancing Sustainability and Ethical Practices
Consumers and regulators are increasingly demanding sustainable and ethically sourced products. Blockchain provides the transparency needed to verify and report on these practices. Companies can record and share information about their sustainability efforts, such as sourcing materials from certified suppliers, reducing carbon emissions, and ensuring fair labor practices.
This transparency helps companies build trust with consumers and meet regulatory requirements. For instance, a fashion brand can use blockchain to prove that its products are made from sustainably sourced materials and produced under fair labor conditions. This not only enhances the brand’s reputation but also attracts a growing segment of environmentally and socially conscious consumers.
Case Studies of Blockchain in Supply Chains
Several companies are already leveraging blockchain to transform their supply chains. IBM’s Food Trust, for example, uses blockchain to enhance food safety and traceability for retailers like Walmart and Carrefour. By providing real-time access to supply chain data, IBM Food Trust helps these companies ensure the quality and safety of their products.
Similarly, Maersk’s TradeLens platform uses blockchain to improve the transparency and efficiency of global shipping. TradeLens provides a secure and transparent way to share shipping information among all stakeholders, reducing paperwork, cutting down on delays, and lowering costs.
Challenges and Future Directions
Despite its potential, blockchain adoption in supply chains faces several challenges. These include technological barriers, such as integrating blockchain with existing systems, and regulatory hurdles related to data privacy and cross-border transactions. Additionally, achieving industry-wide adoption requires collaboration among diverse stakeholders, which can be difficult to coordinate.
However, as technology matures and more companies recognize its benefits, blockchain is expected to become a standard component of supply chain management. Innovations like hybrid blockchains, which combine the strengths of public and private blockchains, and advancements in scalability and interoperability, will further enhance blockchain’s applicability and effectiveness.
Conclusion
In 2024, blockchain is revolutionizing supply chain transparency by enhancing traceability, reducing fraud, improving efficiency, and promoting sustainability. As more companies adopt this technology, supply chains will become more transparent, resilient, and efficient, benefiting businesses, consumers, and society at large. While challenges remain, the ongoing advancements in blockchain technology and growing demand for transparency and accountability promise a bright future for blockchain-enabled supply chains.